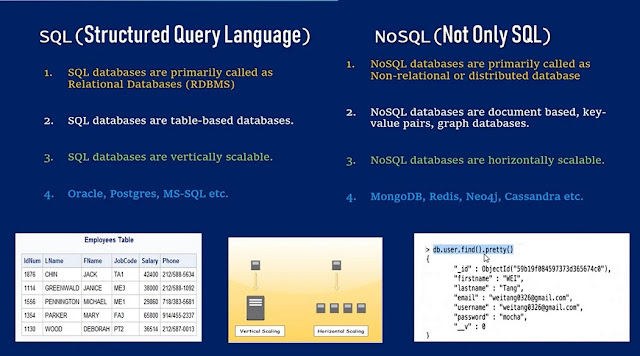
NoSQL, as many of you may already know, is
basically, a database used to manage huge sets of unstructured data, where in
the data is not stored in tabular relations like relational databases. Most of
the currently existing Relational Databases have failed in solving some of the
complex modern problems like :
- Continuously changing nature of
data - structured, semi-structured, unstructured and polymorphic data.
- Applications now serve millions
of users in different geo-locations, in different timezones and have to be
up and running all the time, with data integrity maintained
- Applications are becoming more
distributed with many moving towards cloud computing.
NoSQL plays a vital role in an enterprise
application which needs to access and analyze a massive set of data that is
being made available on multiple virtual servers (remote based) in the cloud
infrastructure and mainly when the data set is not structured. Hence, the NoSQL
database is designed to overcome the Performance, Scalability, Data Modelling
and Distribution limitations that are seen in the Relational Databases.
What is Structured
Data?
Structured data is usually text files, with
defined column titles and data in rows. Such data can easily be visulaized in
form of charts and can be processed using data mining tools.
What is Unstructured
Data?
Unstructured data can be anything like video
file, image file, PDF, Emails etc. What does these files have in common,
nothing. Structured Information can be extracted from unstructured data, but
the process is time consuming. And as more and more modern data is
unstructured, there was a need to have something to store such data for growing
applications, hence setting path for NoSQL.
NoSQL Database Types
Following are the NoSQL database types :
- Document Databases : In
this type, key is paired with a complex data structure called as Document.
Example : MongoDB
- Graph stores : This
type of database is ususally used to store networked data. Where in we can
relate data based on some existing data.
- Key-Value stores : These
are the simplest NoSQL databases. In this each is stored with a key to
identify it. In some Key-value databases, we can even save the typr of the
data saved along, like in Redis.
- Wide-column stores : Used to store large data sets(store columns of data together). Example : Cassandra(Used in Facebook), HBase etc.